What is the difference between side scatter and forward scatter? And what are people talking about when they say drop delay?
This list of flow cytometry definitions will give you the vocabulary to start understanding the basics of flow cytometry.
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
L
P
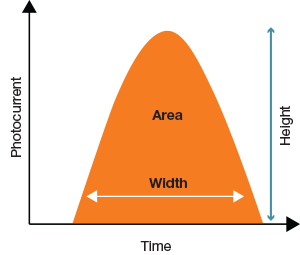 Height: The maximum amount of current output by the photo multiplier tube (PMT)
Height: The maximum amount of current output by the photo multiplier tube (PMT)
Area: The integral of the pulse
Width: The time interval during which the pulse occurs
Signal intensity can be measured by either height or area
The width parameter measures the time that the cell spends in the laser
Quantifying a pulse by measuring its height, area, and width.
S
T
Y
See how the S3e™ Cell Sorter can simplify cell sorting and download our Flow Cytometry Basics Guide for an introduction to flow cytometry and cell sorting.

