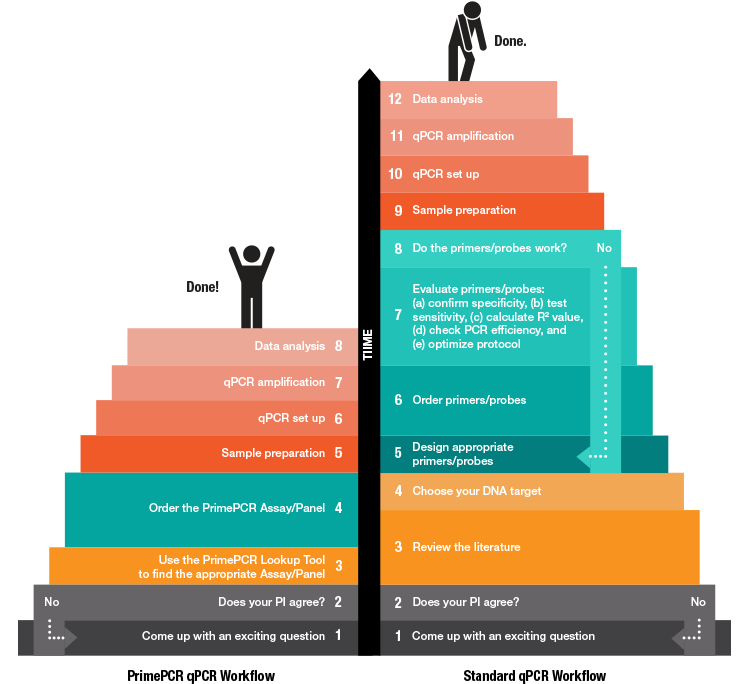
Did you know that you can eliminate at least four steps from your qPCR gene expression workflow? That’s right.
With PrimePCR Assays and Panels, we’ve designed primers and probes for your gene expression experiments for you. By doing this, we help you eliminate multiple steps from your reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) gene expression workflow and, in the process, save you a ton of time and frustration.
Primer/Probe Sequence Determined
After you’ve identified your gene of interest, all you have to do is come to the PrimePCR website, search for your gene target, and buy the primers and/or probes you need. No need to scour the literature for a sequence that may or may not work or to design it yourself.
Primers/Probes Designed
To make your life easier, our primers and probes were designed to avoid single nucleotide polymorphisms and secondary structure in primer annealing sites. Also, they are intron-spanning when possible and compatible with up-to-date experimental conditions.
PrimePCR design features
Design Feature | Why It’s Important |
| Maximum transcription coverage | Detects the majority of expressed mRNA transcripts for each gene of interest |
| Intron-spanning assay design when possible | Detects only cDNA and not contaminating gDNA |
| Secondary structure avoided | Secondary structure of cDNA can lead to poor efficiency of the qPCR assay |
| Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) avoided | SNPs in primer and probe annealing sequences can lead to poor assay efficiency |
| Specific sequences identified | Avoids coamplification of nonspecific off-target sequences |
Primers/Probes Tested and Validated
To keep you and, let’s face it, ultimately your PI, happy, we made sure to bench test our primers and probes for specificity, efficiency, linear dynamic range, and primer-dimers. We even used next-generation sequencing to confirm the specificity of the PCR products for every single human, mouse, and rat assay.
PrimePCR validation features
Validation Feature | Why It’s Important |
| 7-point serial dilution | Determines the dynamic range, R2, and efficiency of the assay |
| Amplification of gDNA | Determines whether the assay detects contaminating gDNA |
| Melt curve analysis | Confirms melt profile of expected qPCR product |
| Next-generation sequencing | Confirms specificity of the assay |

