Ribonucleases (RNases) catalyze the degradation of RNA into smaller components, and are ubiquitous in a laboratory environment. While RNases have many essential functions within a cell, they are generally problematic outside the cell acting as a contaminant to researchers working with RNA. Endogenous RNases that co-purify during sample preparation and perspiration from ungloved hands can both contaminate pipet tips, tubes, buffers, water, and surfaces that come in contact with RNA. Researchers combat RNase contamination by using dedicated pipets, aerosol-barrier tips, DEPC-treated water and buffers, and wiping surfaces with RNase-inhibiting agents. Figure 1 shows varying levels of RNase contamination in different preparations of spleen and pancreas RNA. Contaminating RNase in a reverse transcription (RT) reaction can have adverse effects on gene expression analysis. Studies have shown that degraded RNA can cause threshold cycle (CT) delays in quantitative PCR (qPCR), which in turn can significantly affect overall mRNA quantification. Inaccurate representation of target gene levels can result from using degraded mRNA as a template for cDNA synthesis. The impact can be dramatic, especially when there are small differences in the expression levels between control and treated samples.
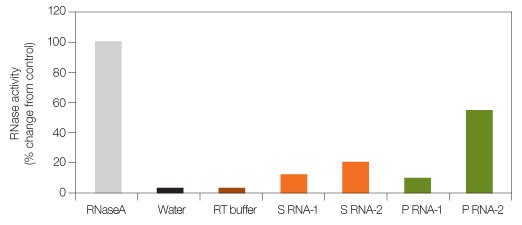
Fig. 1. RNase levels in different RNA samples. RNaseA, water, RT buffer (used to dilute RNaseA), spleen RNA (S RNA-1 and S RNA-2), and pancreas RNA (P RNA-1 and P RNA-2) from two different preparations were assayed for RNaseA activity using a commercially available kit. RNaseA (several fold higher than normally found in contaminated RNA preparations) was used as control to demonstrate varying levels of RNaseA activity in sample preparations.
Not all cDNA synthesis kits have the same capacity to protect the integrity of RNA. An optimal level of RNase inhibitor is critical for powerful RNase inhibition and efficient reverse transcription. The iScript™ cDNA synthesis kit comes with a 5x iScript reaction mix and iScript reverse transcriptase, which is also blended with a potent RNase inhibitor. Figure 2 shows how the iScript cDNA synthesis kit significantly inhibits RNase activity.
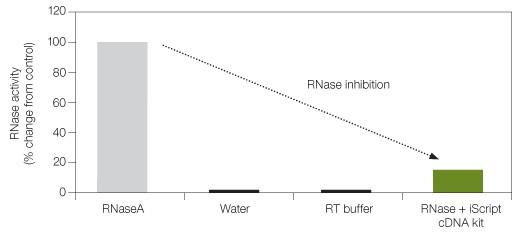
Fig. 2. RNase inhibition with iScript cDNA synthesis kit. RNaseA, water, RT buffer (used to dilute RNaseA), and RNase + iScript cDNA kit were assayed for RNaseA activity using a commercially available kit. RNaseA (several fold higher than normally found in contaminated RNA preparations) was used as control to assess the effect of inhibition by the iScript cDNA kit.
To demonstrate the functional relevance of RNase inhibition in RT-qPCR, an experiment was performed with spiked RNaseA and appropriate controls (Figure 3).
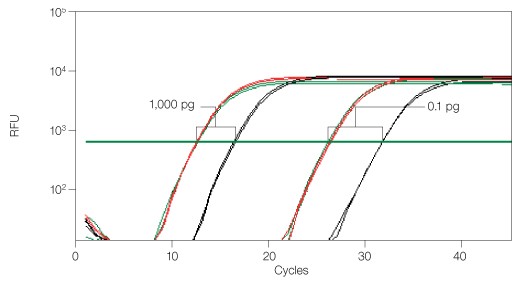
Fig. 3. Functional RT-qPCR assay demonstrating RNaseA inhibition by iScript cDNA synthesis kit. 18S rRNA was amplified using iQ™ SYBR® Green supermix. Reverse transcription (RT) performed with iScript (—); RT performed with spiked RNaseA (—); RT performed with RNaseA but no RNase-inhibitor (—). Two RNA inputs (1,000 and 0.1 pg) were reverse transcribed for all three groups. The cDNA synthesis reaction with RNase but no RNase-inhibitor showed significant CT delay (3–5), whereas the iScript kit demonstrates powerful inhibition of RNaseA. RFU, relative fluorescence units.
There was no CT delay between cDNA synthesis performed without RNaseA and cDNA synthesis performed with spiked RNaseA (<0.5 CT difference), showing powerful inhibition of RNaseA. The iScript cDNA synthesis kit can inhibit contaminating RNases or RNases that co-purify with sample preparation, and allow accurate qPCR quantification of target genes. The two-tube format (5x reaction mix and iScript reverse transcriptase) also reduces the chance for RNaseA contamination during setup.
The benefit of powerful RNaseA inhibition is also offered by our 1-tube (iScript™ reverse transcription supermix for RT-qPCR) and high data throughput (iScript advanced cDNA synthesis kit for RT-qPCR) reverse transcription formats.
For more information, request bulletins 6031 and 6125.
SYBR is a trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc. Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. is licensed by Molecular Probes, Inc. to sell reagents containing SYBR® Green I for use in real-time PCR, for research purposes only. Purchase of IQ™ SYBR® Green supermix includes an immunity from suit under patents specified in the product insert to use only the amount purchased for the purchaser’s own internal research. No other patent rights are conveyed expressly, by implication, or by estoppel. Further information on purchasing licenses may be obtained by contacting the Director of Licensing, Applied Biosystems, 850 Lincoln Centre Drive, Foster City, California 94404, USA.

